Addressing Dallas’ loose dog challenge with a community-driven strategy
Dallas Animal Services (DAS) strives to lead the nation in compassionate animal care while addressing community needs through innovative shelter operations and engagement. In line with their Dallas90 Initiative which launched in 2018, DAS has been working toward a 90% live release rate for adoptable pets. However, increasing intakes prompted a deeper examination of loose dog issues in the city, with an aim to better align their work with community needs.
In late 2023, DAS engaged JVR Strategies (JVR) to assist with assessing the scope of the ongoing loose dog issue and explore potential directions for a multi-year project to reduce stray and loose dogs in Dallas.
What started as a request to assist with a request for proposal, became a more engaging project that brought our team to the streets of Dallas to meet and engage with community members in meaningful ways. Our research led to the creation of the following integrated framework as one model for engaging with the community on loose dog concerns.
Overview of Dallas’s Integrated Community‑Driven Loose Dog Strategy
The Integrated Community Strategy pulls together potential recommendations for a future multi-year project to address loose dog concerns in Dallas. The Foundational Components are strategies that may be viewed from a Community-Centered Framework.
Integrated Community Strategy
A comprehensive approach that combines targeted actions with community-driven
collaboration to address the loose dog issue sustainably.
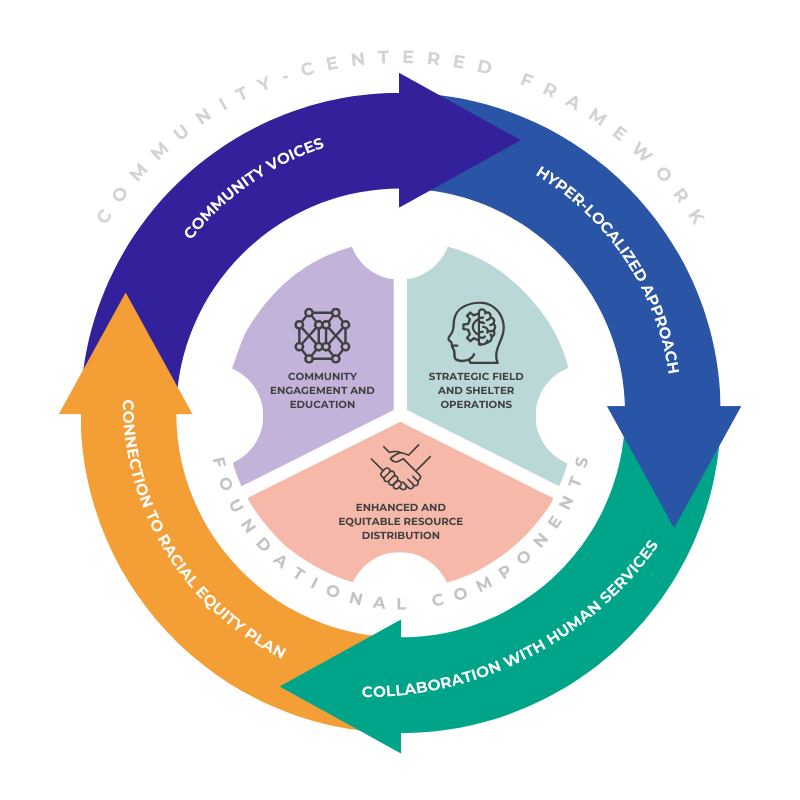
The Foundational Components present potential strategies and resources to help mitigate the loose dog problem and related challenges, as presented in conversations and survey responses. The Community-Centered Framework emphasizes collaboration with neighborhoods with the goal of aligning solutions to reflect local values and needs. Together, these two parts offer a view to consider as the city develops a plan to address immediate concerns while building a foundation for community-driven, and community-supported outcomes.
Integrated Community Strategy in Detail
Community-Centered Framework
The Community-Centered Framework is a guiding approach that emphasizes collaboration and co-creation with Dallas neighborhoods. This framework focuses on listening to community voices, understanding local values, and involving residents in shaping solutions that reflect their unique experiences and needs. Prioritizing relationship-building can foster trust, support community engagement, and create a foundation for ongoing, community-driven efforts. The framework serves as a bridge, helping to align DAS’s initiatives with the perspectives of residents and promoting a connected and culturally responsive approach to animal control.
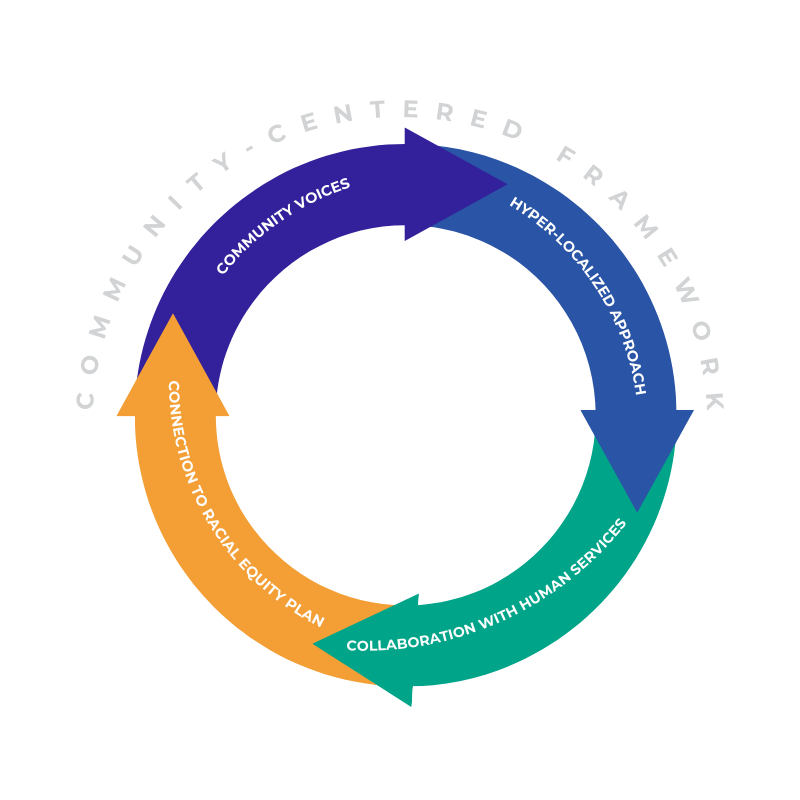
Community Voices
- Listening and Co-Creating Solutions: Consider a Community Voice Model1 as one approach to align DAS’s strategies with local residents’ needs and values similar to the Virginia Community Voice model.
- Building Trust Through Consistent Presence: Establish a consistent presence to improve collaboration and trust, especially in areas with historical distrust of authorities. Trust-building improves DAS’ ability to work with the community on animal control initiatives. Community feedback from interviews and ride-alongs underscored the importance of trust and relationship-building.
Hyper-Localized Approach
- Create Neighborhood-Specific Response Plans: Develop tailored response plans for individual neighborhoods by working with local residents. Co-creating these plans helps ensure they align with each neighborhood’s unique needs.
- Focus on Economic and Demographic Variability: Prioritize neighborhoods experiencing economic hardship or high loose dog incidents with tailored interventions that reflect their challenges.
Collaboration with Human Services and City Departments
- Interconnected Support Model: Work alongside other city departments, such as Health, Housing, and Sanitation, to provide a coordinated response to the loose dog issue. This model promotes a supportive environment by addressing the intersecting human and animal welfare needs in neighborhoods facing economic and social challenges.
Connection to Racial Equity Plan
- Equitable Access to Pet Resources: Ensure that resources are distributed fairly across neighborhoods, prioritizing areas with historically limited access to veterinary and containment resources.
- Inclusive Community Engagement: Actively involve community members in the planning and implementation of solutions, particularly in neighborhoods with a history of skepticism toward animal control interventions, to increase buy-in and cooperation.
- Alignment with Racial Equity Plan: Regularly review and align interventions with the city’s Racial Equity Plan, focusing on the impact of enforcement and resource distribution to prevent unintended consequences that could exacerbate existing inequities.
Foundational Components
The Foundational Components focus on three key areas: community engagement and education, equitable resource distribution, and strategic field & shelter operations. Each component includes potential recommended programs, initiatives, and resources aimed at reducing the loose dog population, improving community safety, and promoting responsible pet ownership. These foundational strategies are not exhaustive; other approaches may also be effective and should be considered as part of a broader response.
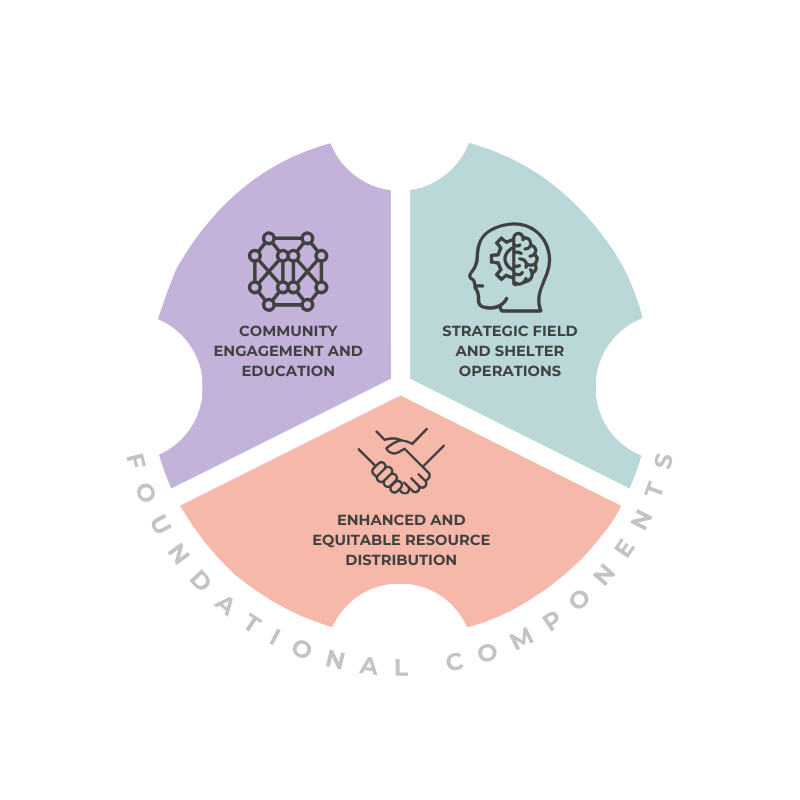
Community Engagement and Education
- Public Figures and Local Influencers: Leverage trusted public and community figures, such as former Dallas Cowboys players and local community leaders, to influence attitudes toward pet ownership. Utilizing familiar faces could amplify messages and strengthen public resonance.
- Accessible Educational Resources: Offer accessible educational resources like informational signage, workshops, and community events to support public understanding toward responsible pet ownership and humane animal treatment.
- Community Advisory Boards and Volunteer Programs: Establish community advisory boards and volunteer opportunities for residents to participate actively in shaping initiatives, strengthening local ties, and building collective responsibility.
- Partnerships with Local Organizations and Stakeholders: Collaborate with trusted local groups to expand reach, connect with residents effectively, and ensure that initiatives are rooted in the neighborhood’s cultural context.
- Localized Outreach and Community Connection Events: Host events and localized outreach initiatives that bring together community members, DAS, and other city services to foster a sense of shared mission and responsibility.
- Owner Education: Raise awareness and understanding of responsible pet ownership, including containment practices, spay/neuter benefits, and pet identification options like microchipping.
Enhanced and Equitable Resource Distribution through Partnerships with Human Services
- Resource-Based Support: Increase access to a variety of resources that support pet ownership, particularly in economically disadvantaged areas. This includes pet food pantries, supply assistance (leashes, collars, bedding), mobile veterinary clinics, and pop-up care events providing low-cost or free preventive care. Offer pet identification kits and services like ID tags and microchipping vouchers to assist with lost pet recovery. Free or low-cost behavioral support and training programs, as well as fencing repair assistance.
- Collaborative With Human Services: Partner with human services such as Housing, Health, and Sanitation to provide a coordinated response to the interconnected needs of residents and their pets. This includes working with housing authorities and landlords to promote pet-friendly rental housing, reduce pet-related fees, and support tenants in accessing affordable, pet-inclusive housing options.
- Spay/Neuter and Veterinary Services: Expand access to spay/neuter services and basic veterinary care, particularly in areas with high stray populations. Address barriers to accessible care such as cost, transportation, hours of operation, and language. Leverage community members to promote and help run events.
- Neighborhood-Led Programs: Establish neighborhood-led networks to support local pet owners through guidance, and connection to resources. These peer-led networks can also facilitate lost pet recovery and reunification efforts. Offer tools, training, and a locally administered registry or platform (Nextdoor, Facebook page, etc.) for reporting sightings and coordinating reunifications.
Strategic Field and Shelter Operations
- Response Capacity and Efficiency: Increase DAS field capacity to address loose dog complaints in a timely manner. This may include additional field officers, faster response times, and an increased community presence to mitigate risks associated with loose dogs.
- Balanced Shelter Intake and Field Operations: Implement sustainable strategies for shelter stray intake that do not overwhelm DAS resources. This includes setting intake prioritization criteria, fostering clear communication between field officers and shelter staff, and supporting community members to help dogs return home.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Utilize data to identify patterns, assess needs, and refine response priorities. This includes mapping hotspots and analyzing fluctuations in call volumes to allocate resources effectively.
- Clear Communication of DAS Roles and Resources: Regularly update communities on DAS role and available resources through community meetings and digital platforms. Transparent communication fosters community trust and aligns DAS goals with residents’ expectations.
- Relationship-Focused Field Operations: Encourage field officers to foster positive relationships with residents, emphasizing respect for local contexts. Providing non-punitive options, like educational warnings, can help improve compliance and goodwill.
- Community-Recommended Enforcement and Policy Enhancements: Expand capturing policy suggestions offered by residents to strengthen containment and owner responsibility.
Advancing Dallas’ Community‑Driven Loose Dog Strategy
Addressing the loose dog issue in Dallas is not merely an animal control challenge but a complex intersection of public safety, equity, and community welfare. By integrating a community-centered framework with targeted, data-driven solutions, Dallas Animal Services has the opportunity to lead with innovation and compassion, setting a national standard for tackling such multifaceted challenges.
This work matters because it extends beyond managing animal populations—it seeks to strengthen the human-animal bond while fostering trust and equity within Dallas’s diverse communities. The recommendations presented here serve as an initial framework to create community-driven outcomes that address the root causes of the problem, promote public safety, and ensure that resources are distributed equitably. Aligning these efforts with the City’s Racial Equity Plan ensures that the solutions offered will prioritize inclusivity and cultural responsiveness for City residents and their pets.
Through collaboration, education, and systemic change, the City of Dallas can transform its approach to loose dogs into a model of compassionate and equitable animal welfare. These efforts will not only enhance the lives of pets and their owners but will also contribute to the overall health, safety, and resilience of the City as a whole.
Read the Executive Summary: City of Dallas Loose Dog Community Project Report to learn more about how JVR approached this community project.
- Virginia Community Voice. “Our Model.” Accessed November 4, 2024. https://vacommunityvoice.org/ ↩︎
